The 2019 update includes a complete revision of the section on monitoring asthma including new information on predicting future risk of asthma attacks and updates to the sections on pharmacological management of asthma supported self management non pharmacological management of asthma and management of acute asthma in adults and children.
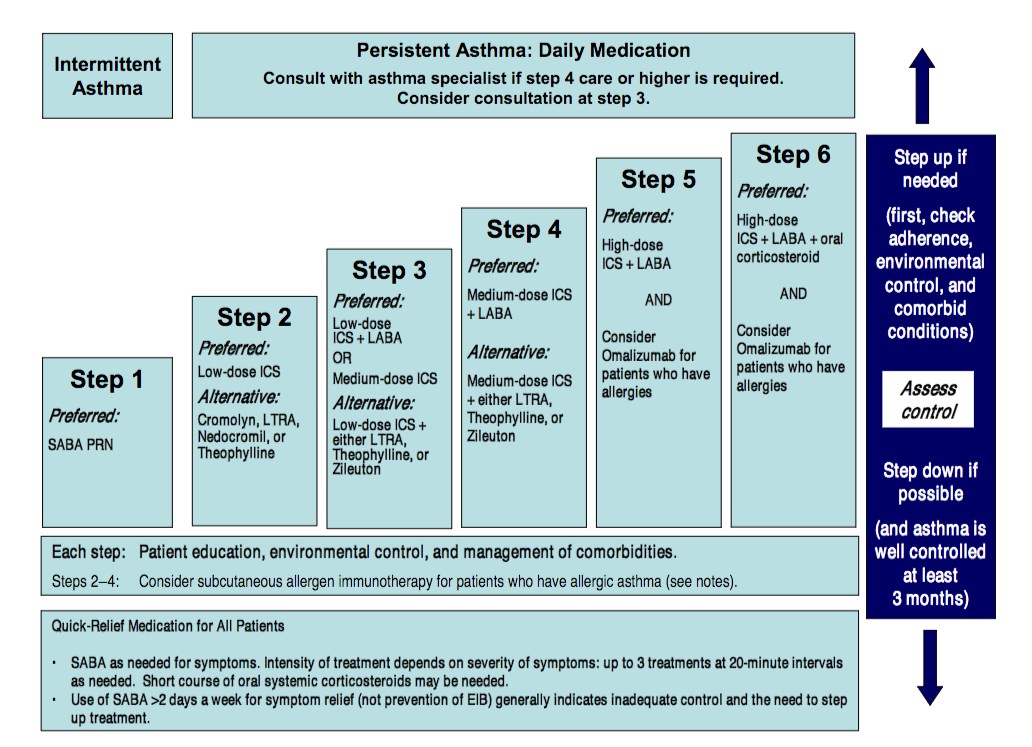
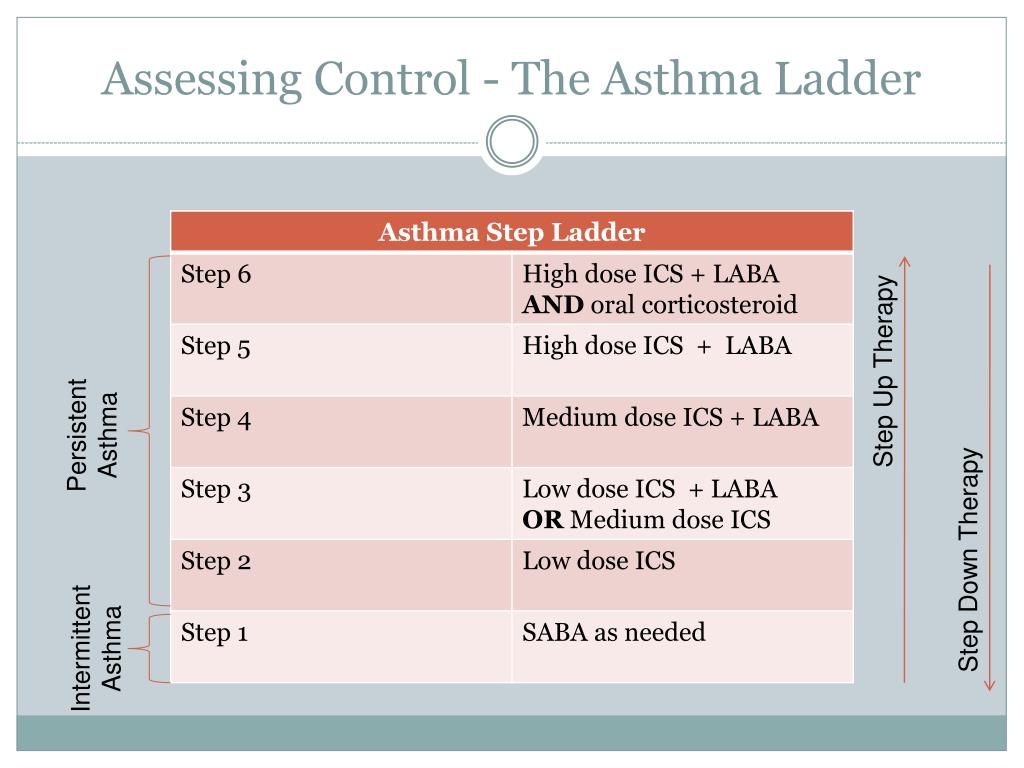
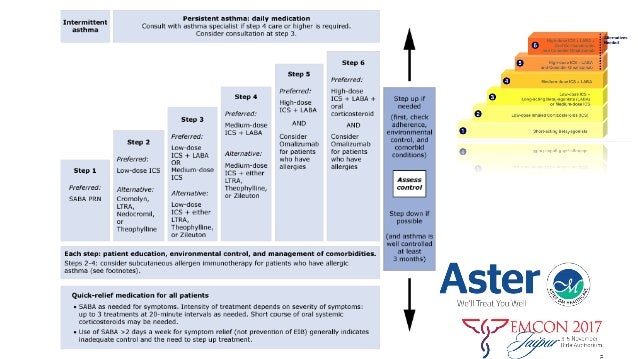
Asthma step up ladder.
Consider short course oral corticosteroid.
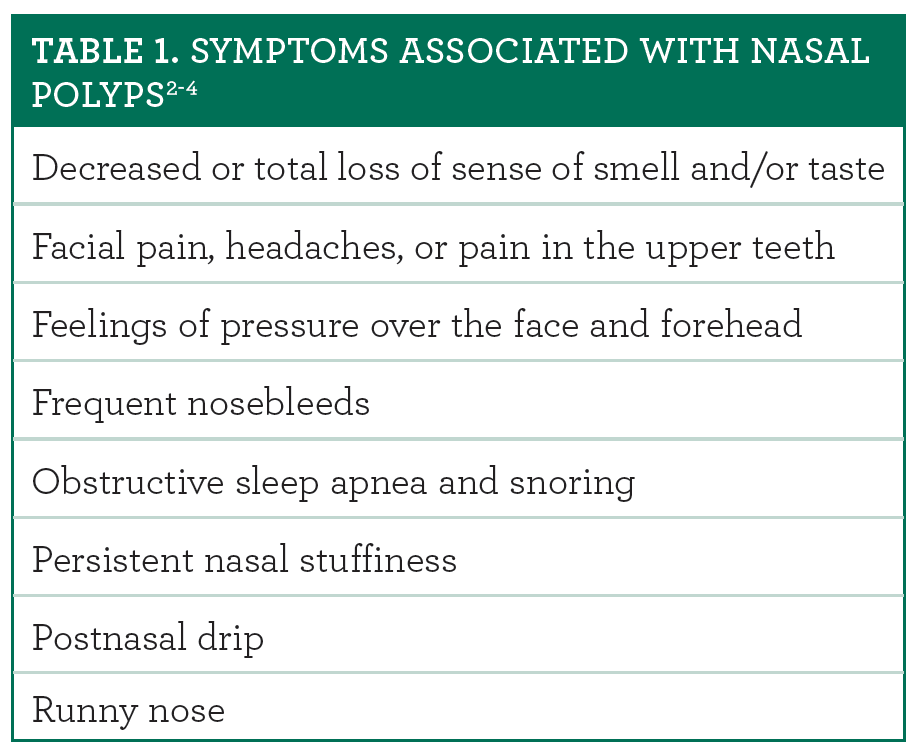
Asthma causes sympt oms such as wheezing shortness of breath chest tightness and cough that vary over time in their occurrence.
Step down if possible.
Re evaluate in 2 6 weeks.
Step up 1 step.
British guideline on the diagnosis and management of asthma.
This guidelines summary is part of a series of summaries of the british thoracic society scottish intercollegiate guidelines network guideline 158.
Follow up after an exacerbation.
Determine if therapy should be adjusted.
Step up 1 2 steps.
Re evaluate in 2 weeks.
Asthma is highly variable over time.
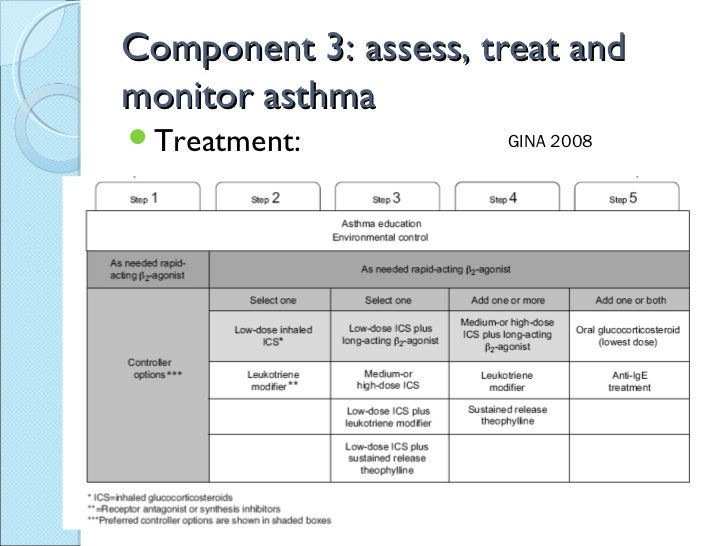
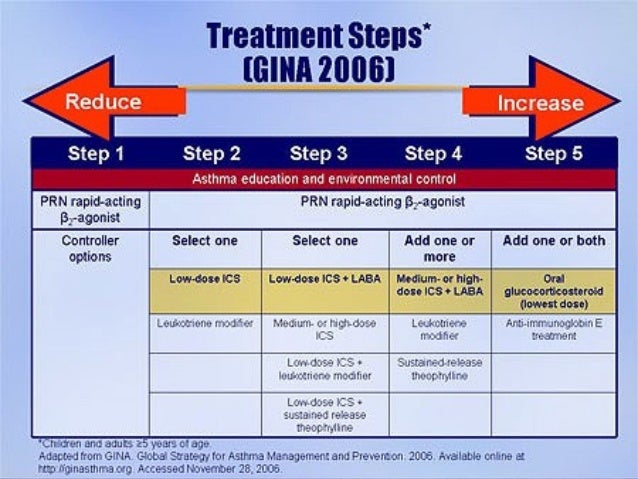
Step 1 occasional relief of symptoms as required inhaled short acting b 2 agonist given to all patients step 2 inhaled corticosteroid ics beclometasone or budesonide 200mcg twice daily if using qvar 100mcg twice daily step 3 long acting b 2 agonist laba formoterol 12mcg twice daily or salmeterol 50mcg twice daily 4 week trial.
Every 2 6 weeks while gaining control every 1 6 months to monitor control every 3 months if step down in therapy is anticipated use of medications.
This summary focuses on recommendations for the management of asthma in adults including diagnosis monitoring pharmacological management and management of acute asthma.
32 glossary of asthma medication classes.
Step up if needed.
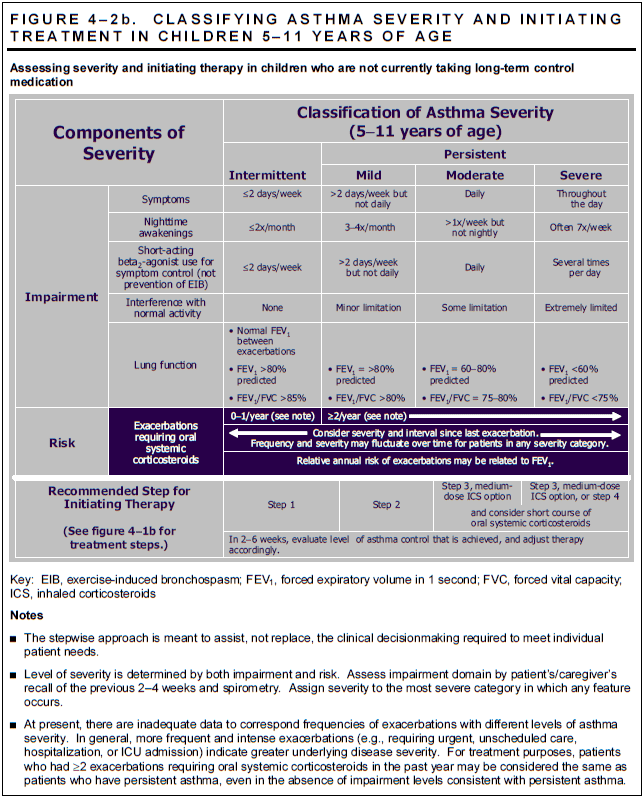
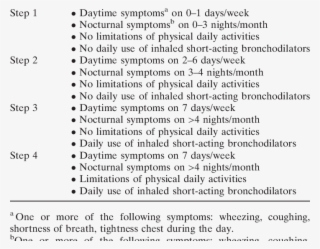
A stepwise step up if necessary and step down when possible approach to asthma management continues to be used in the current guidelines and is now divided into 3 groups based on age 0 4 y 5 11.