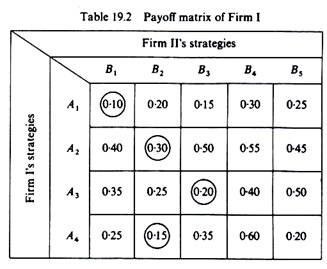
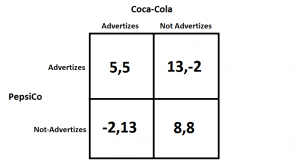
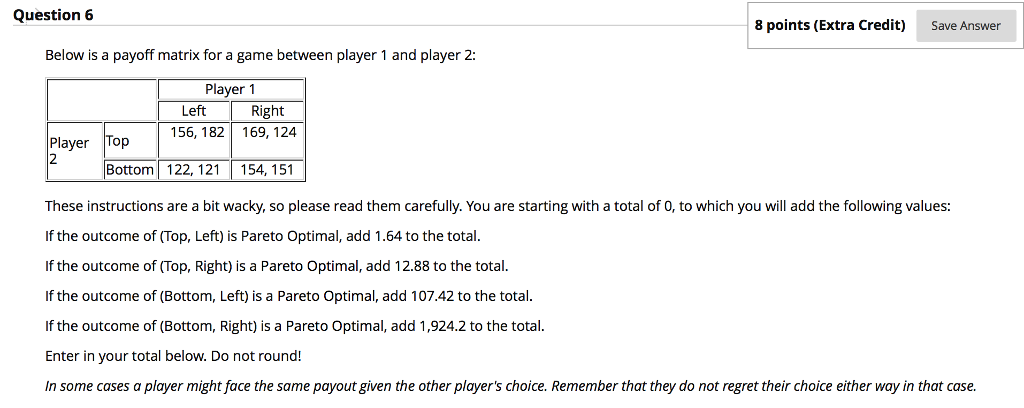
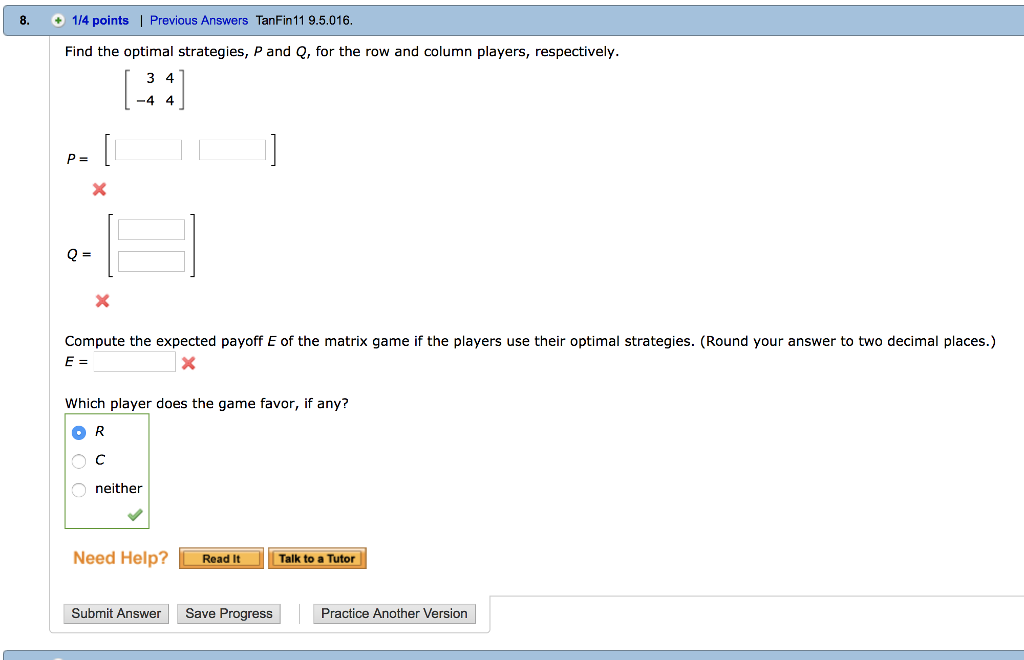
In game theory a payoff matrix is a table in which strategies of one player are listed in rows and those of the other player in columns and the cells show payoffs to each player such that the payoff of the row player is listed first.
How to read payoff matrix.
There are 2 firms a and b and they want to decide whether to start a new campaign.
It is common practice to show the row player s payoff first and the column player s payoff second.
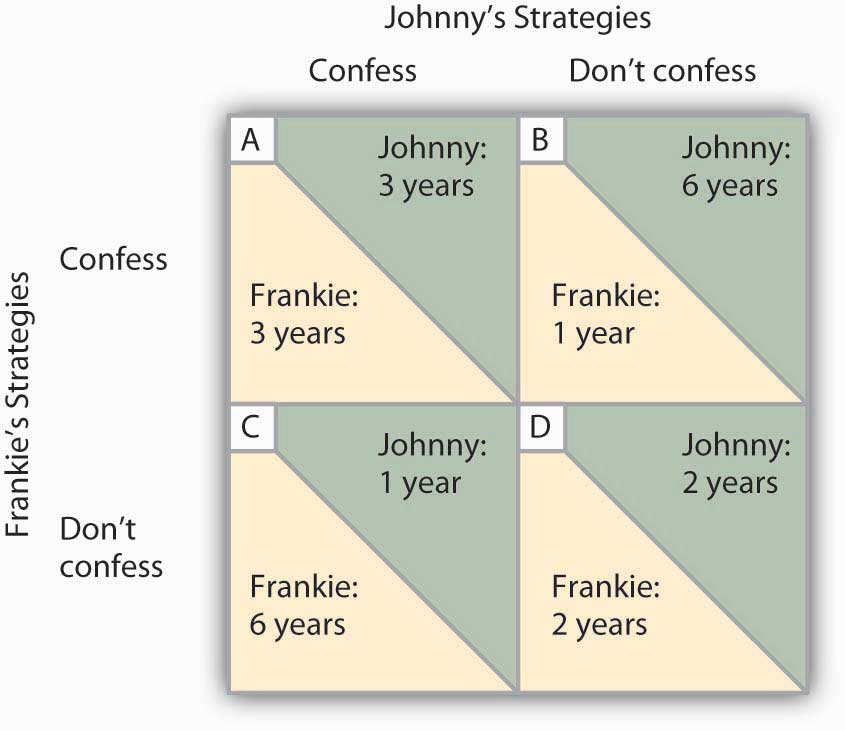
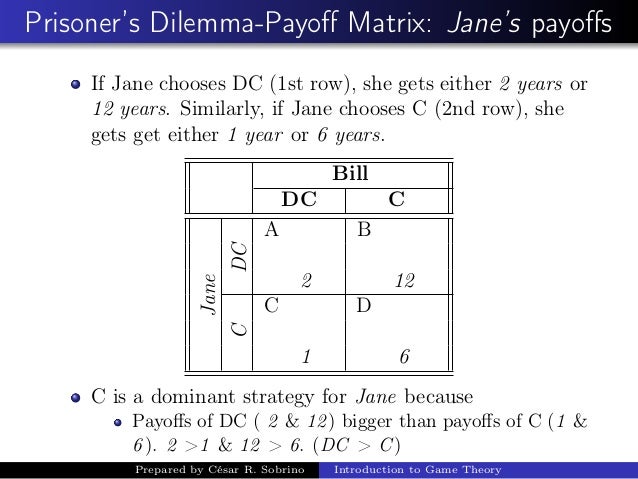
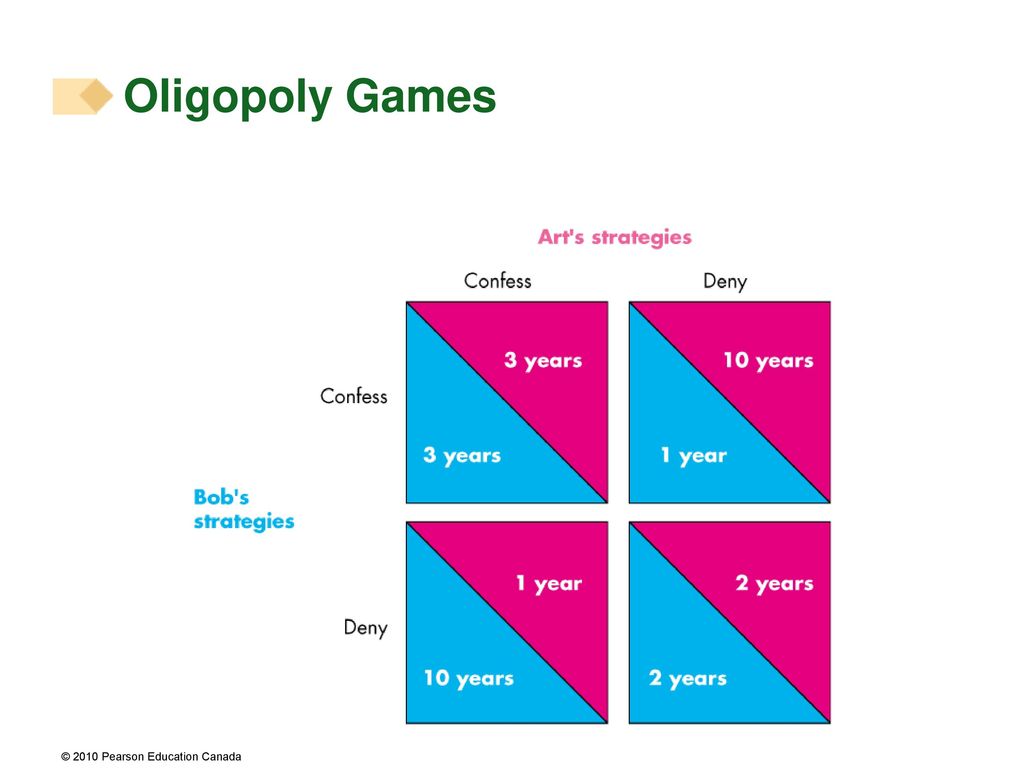
As shown in table 9 the two individuals have two options either to confess or remain silent.
Once this is done it is easy to pick the alternative action whose representative number is better than the other alternative actions representative numbers.
A payoff matrix can be used to calculate the aggregate outcome and to predict a strategy.
Indeed cell d offers the lowest combined prison time of any of the outcomes in the payoff matrix.
Payoff of a game is incremental gain benefit or loss cost that accrue to a player by executing its strategy given the strategy of the other player.
How to read a payoff matrix.
They can either bid 0 1 or 2 dollars.
The payoff matrix in the present case is shown in table 9.
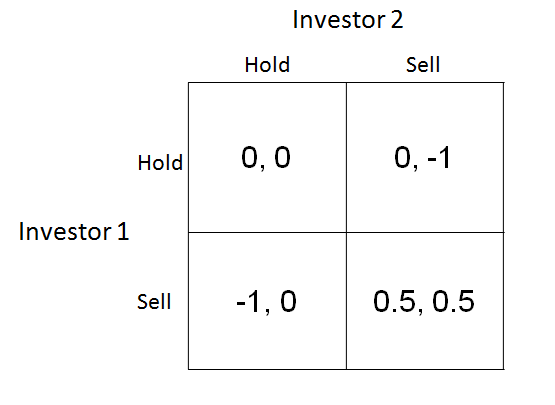
The cell with both payoffs circled is a nash equilibrium.
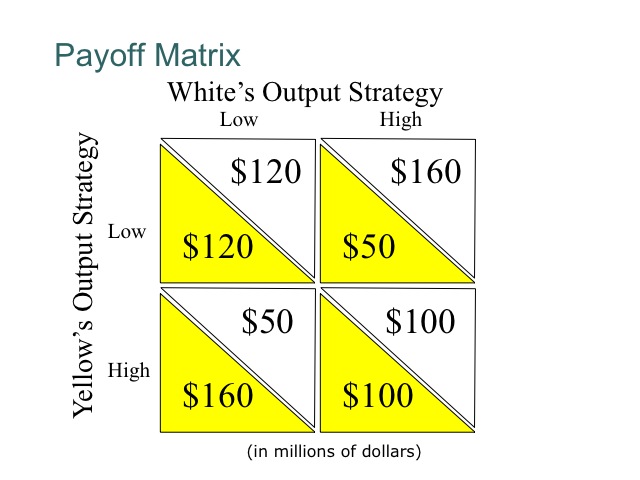
Start a new campaign.
Game theory eg payoff matrix for a new technology game firm b.
A decision rule converts this row of payoffs into a single number that somehow represents the whole row.
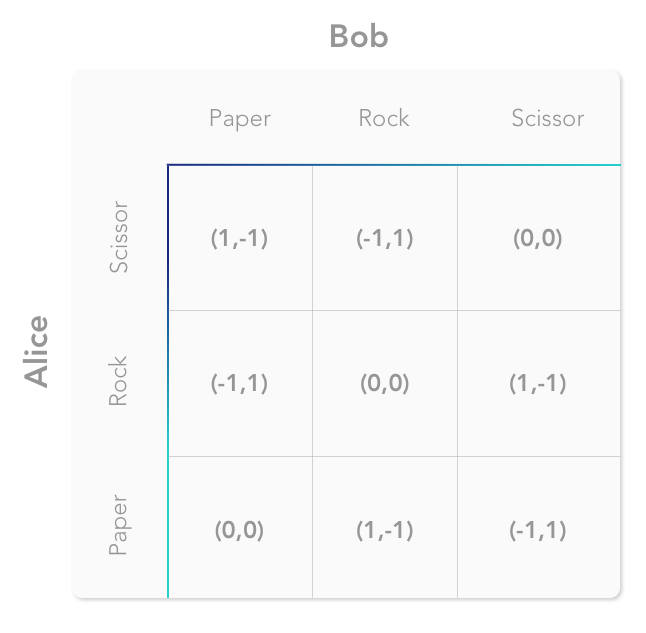
Since both players have 3 options we know that their are nine possible outcomes.
Of course the outcome of the game depends on the way the payoff matrix is structured.
A payoff matrix includes data for opponents strategies and outcomes.
We know that this payoff matrix will be 9 cells and will be a 3x3 matrix because each player has three choices.
Outline its three basic parts.
The decision of confessing by both the individuals depends on the period of imprisonment.
The same method for column player shows that they would not want to switch as well so we can circle their payoff in red.
Payoff tables a profit table pay off table can be a useful way to represent and analyse a scenario where there is a range of possible outcomes and a variety of possible responses.
The payoff matrix assigns each alternative action a row of possible payoffs.
Remember that it is possible to have a payoff matrix with no nash equilibrium.
The best option for both of them is to remain silent.
We can do the same analysis with each choice to see where all of the circles should go.
A pay off table simply illustrates all possible profits losses and as such is often used in decison making under uncertainty.
Start a new campaign.