Binding price floors set below the point at which marginal revenue cost equals willingness to pay increase quantity sold.
If a price floor is not binding then there will be.
Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 100 and go down until you the price floor price or the equilibrium price.
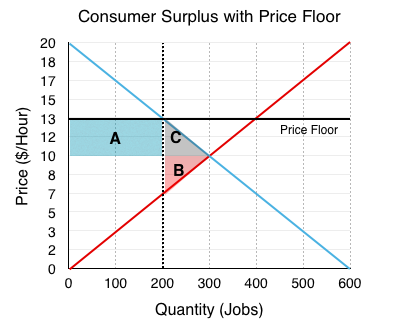
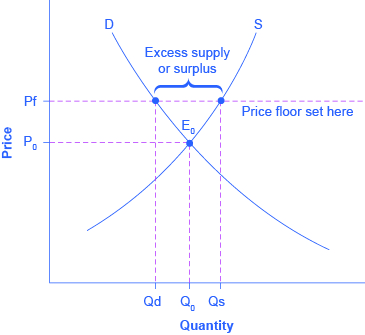
After the establishment of the price floor the market does not clear and there is an excess supply of amount qs qd.
The market will be less efficient than it would be without the price ceiling.
Get more help from chegg.
Get 1 1 help now from expert economics tutors.
There will be a shortage in the market.
A price floor will be binding only if it is set.
B there will be a shortage in the market.
Iii is set at a price above the equilibrium price.
If a price floor is not binding then a there will be a surplus in the market.
If a price floor is not binding then the equilibrium price is above the price floor.
C there will be no effect on the market price or quantity sold.
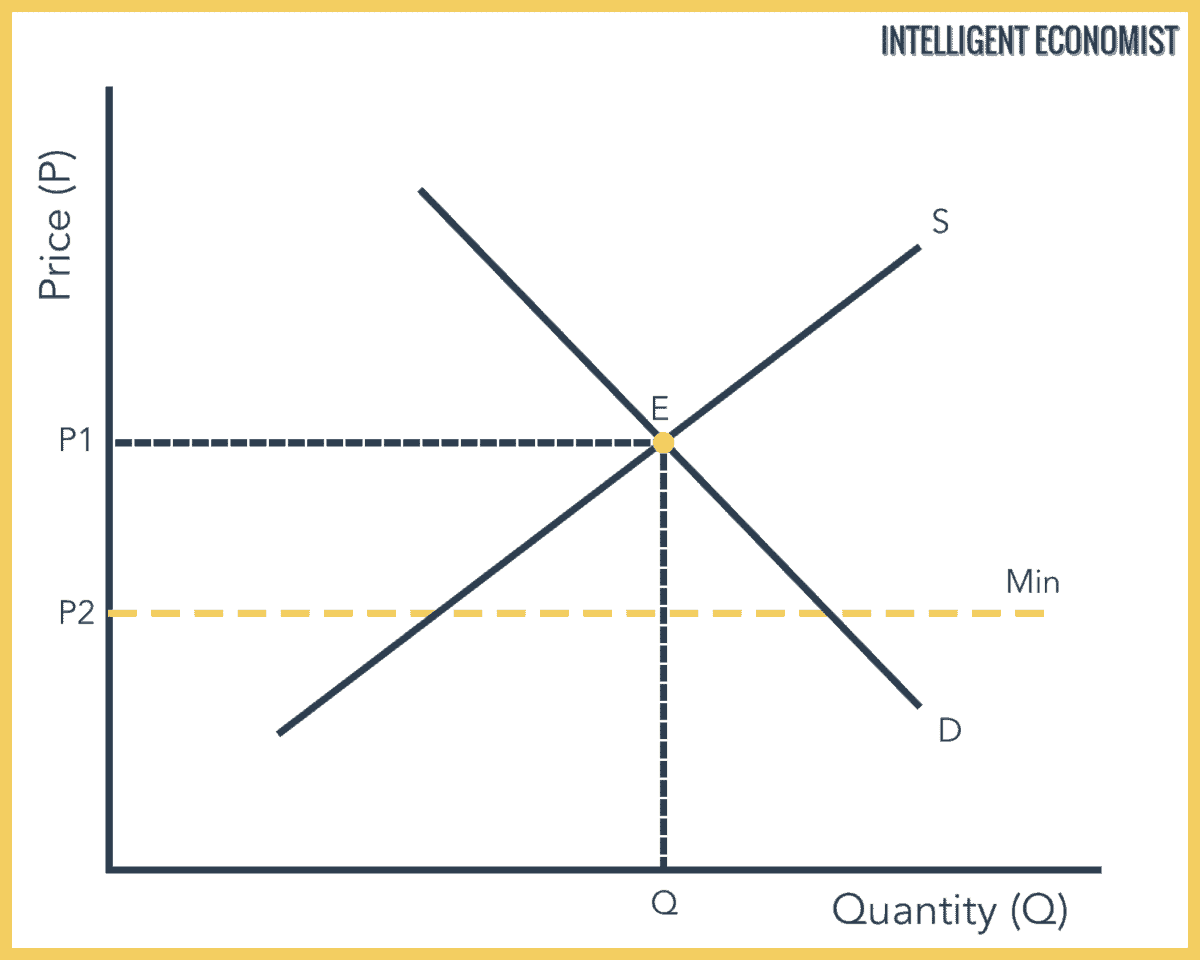
Note that the price floor is below the equilibrium price so that anything price above the floor is feasible.
Suppose there is no price floor or a non binding price floor in a monopsonistic market.
The equilibrium price is below the price floor there will be a surplus in the market.
The equilibrium price is above the price floor.
If a price ceiling is not binding then a.
It has no legal enforcement mechanism.
If a price floor is not binding then 12.
The latter example would be a binding price floor while the former would not be binding.
Decrease and the quantity sold in the market will increase.
There will be no effect on the market price or quantity sold.
D the market will be less efficient than it would be without the price floor.
A binding price floor i causes a surplus.
Then the marginal revenue cost of buying a unit is greater than what sellers would be willing to sell the unit for.
If the government removed a binding price floor from a market then the price paid by buyers will.
Producers are better off as a result of the binding price floor if the higher price higher than equilibrium price makes up for the lower quantity sold.
The equilibrium price is below the price floor.
Above the equilibrium price.
Iv is set at a price below the equilibrium price.
If a price floor is not binding then a.
There will be a shortage in the market.
There will be a surplus in the market.
Ii causes a shortage.